Introduction À LA CINÉMATIQUE
3 Produit mixte¶
Soit x,y et z trois vecteurs, le produit mixte est défini comme suit :
(x,y,z)=x⋅(y∧z) A noter : le produit mixte se conserve par permutation circulaire.
4 Double produit vectoriel¶
1 Produit scalaire¶
Soit x et y deux vecteurs alors
x⋅y=∥x∥⋅∥y∥⋅cos(x,y) avec,
( x,y ) : l’angle orienté de x vers y.
Si x et y sont définis comme suit
x=x1i+x2j+x3ky=y1i+y2j+y3k alors
x⋅y=x1⋅y1+x2⋅y2+x3⋅y3 2 Produit vectoriel¶
Soit x et y deux vecteurs alors
x∧y=∥x∥⋅∥y∥⋅sin(x,y)⋅z avec,
( x,y ) : l’angle orienté de x vers y.
et z vecteur tel que ( x,y,z ) forme un trièdre direct ( z orthogonal aux deux autres vecteurs)
Soit x,y et z trois vecteurs, alors :
x∧(y∧z)=(x⋅z)⋅y−(x⋅y)⋅z 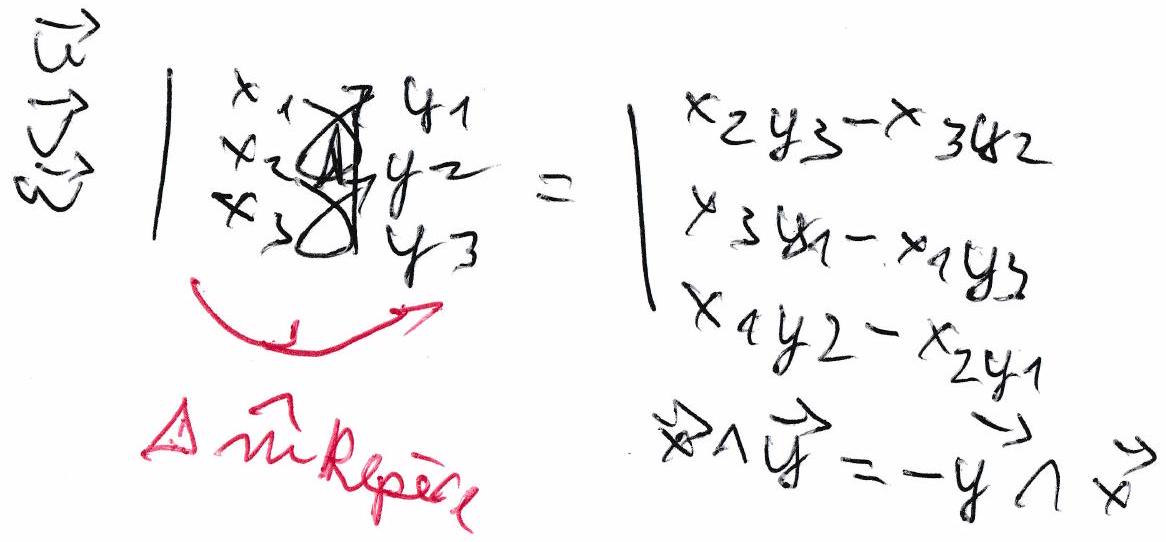
www.lyc-lakanal-sceaux.ac-versailles.fr
